On the night of October 22, Unistellar Citizen Scientists will have the chance to participate in our Network’s first transatlantic (or intercontinental) asteroid occultation!
Main-belt asteroid Loreley will pass in front of a distant star from our view here on Earth, an event known as an occultation. Starting at 10:37 PM UTC, it will be visible in a path across Northern Europe from St. Petersburg, Russia to Swansea, Wales, covering almost all of Estonia, Denmark, central England and Wales.
Across the Atlantic Ocean, the occultation will also be visible from Saguenay, Quebec to Lubbock, Texas in North America, starting at 11:20 PM EDT (10:20 PM CDT). The path also goes through Ottawa, Michigan, Illinois, Missouri, and Oklahoma.
Quick Facts about Loreley
- Located in the asteroid belt, roughly between Mars and Jupiter
- Discovered in 1876 by German–American astronomer Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters
- Named for the Lorelei, a siren from German folklore
- About 112 miles (180 kilometers) across
The Unistellar Network has already made successful detections of Loreley! In July 2020, Unistellar Citizen Astronomer Kevin Voeller detected Loreley from the USA. Earlier this month, Joachim Siegert and Benjamin Mirwald from Germany, as well as Josef Hanus from Czechia, all Citizen Astronomers from the Network, also detected Loreley.
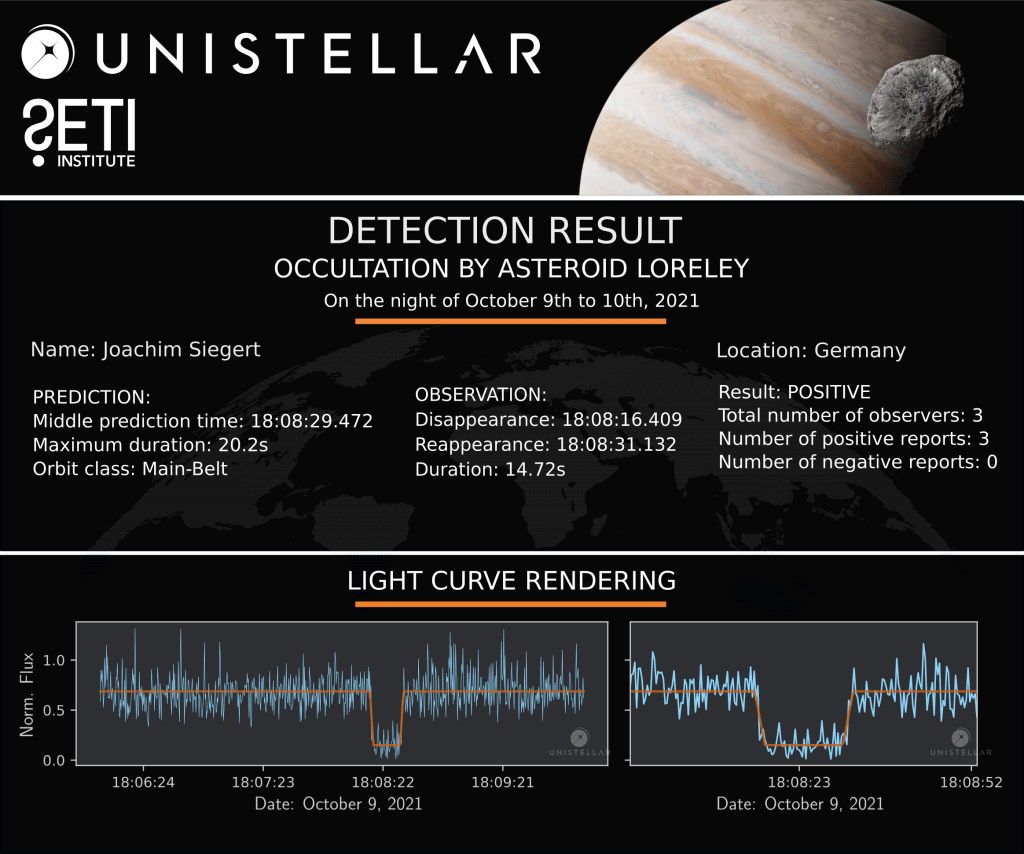
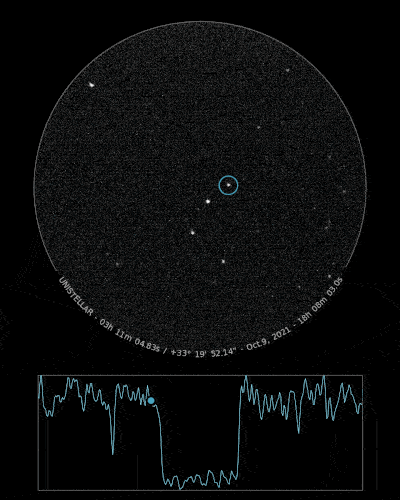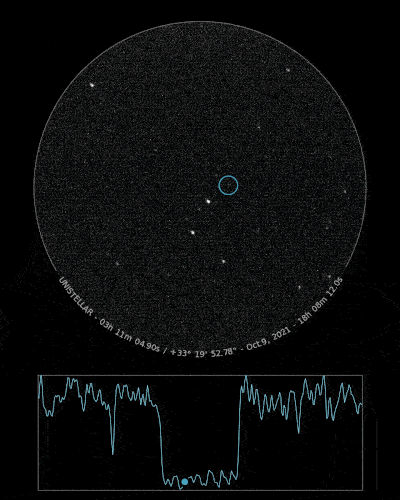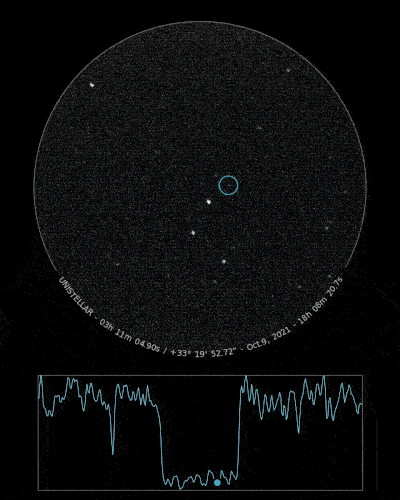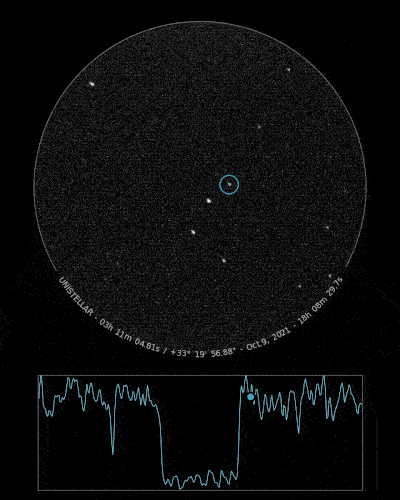
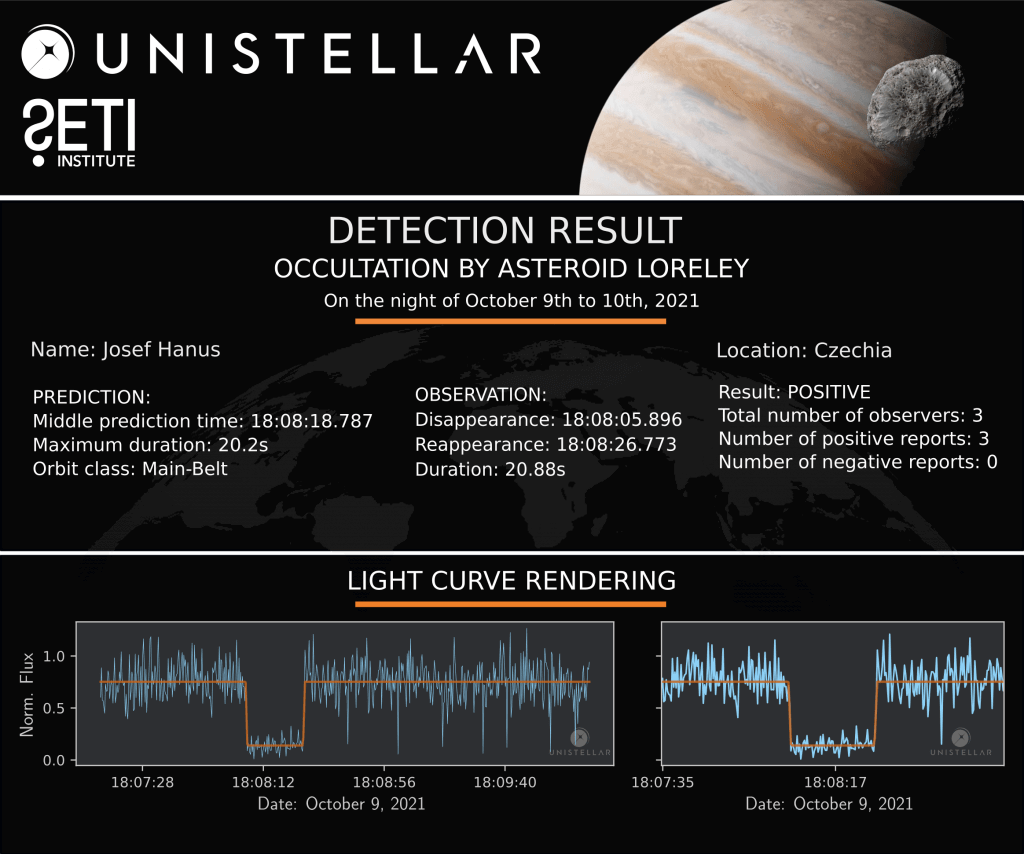
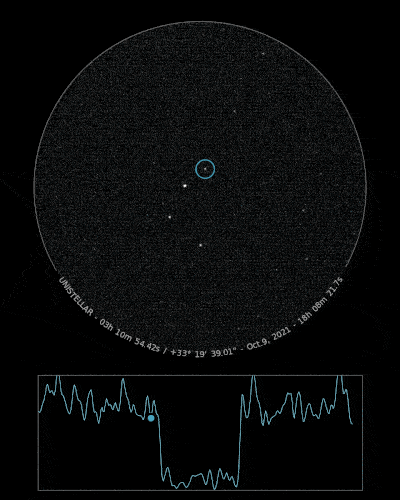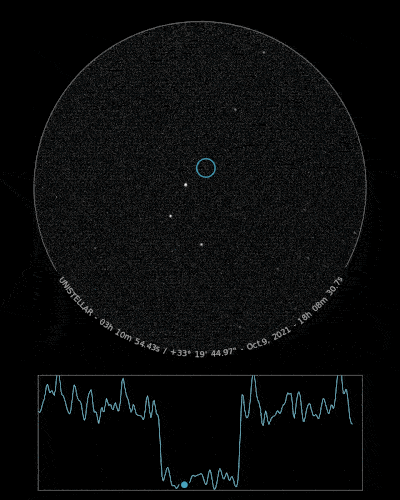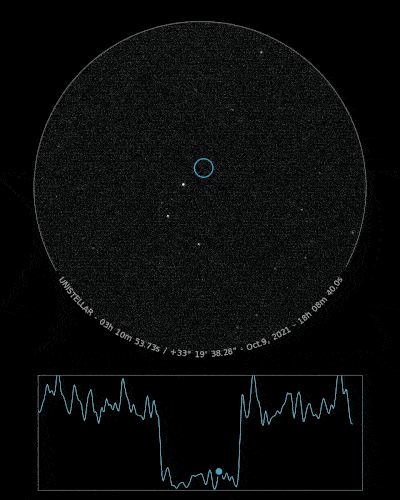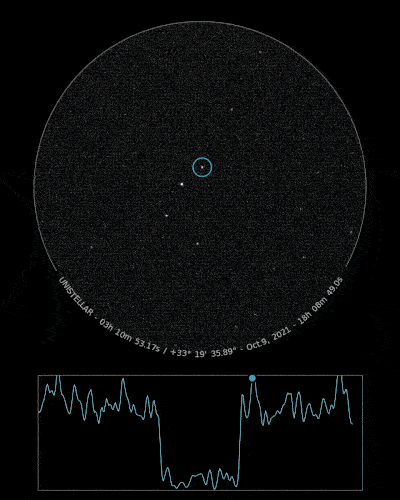
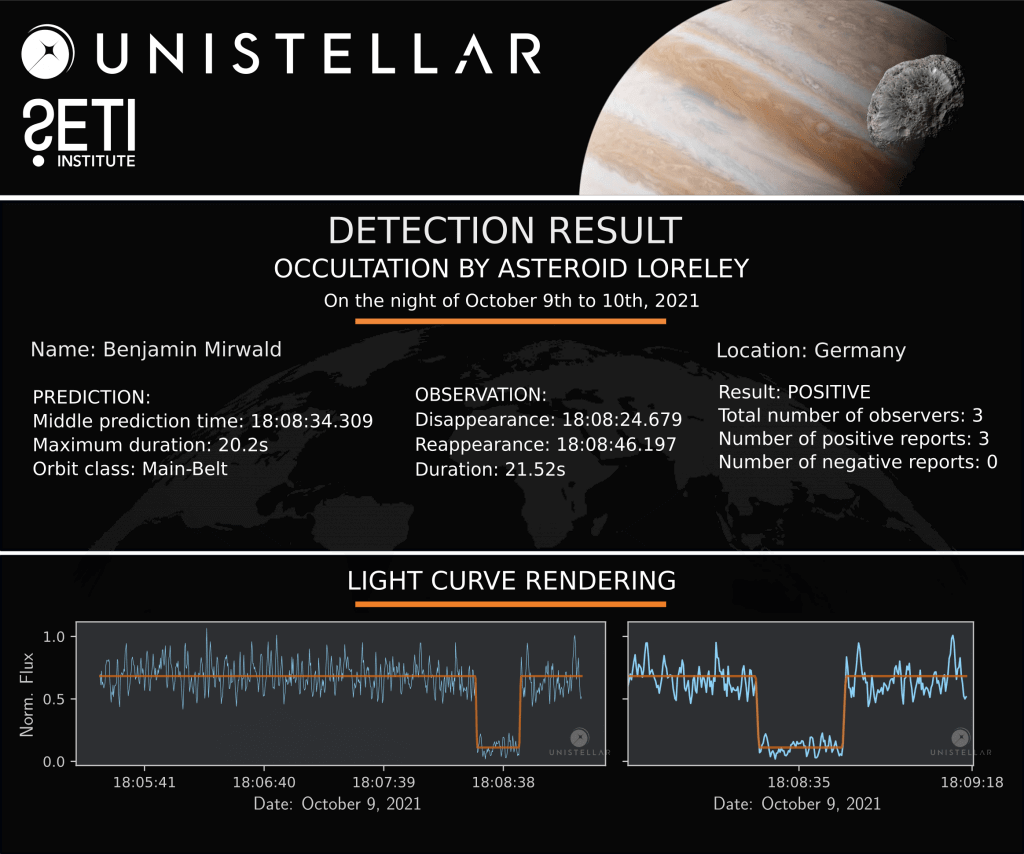
Ready to Observe?
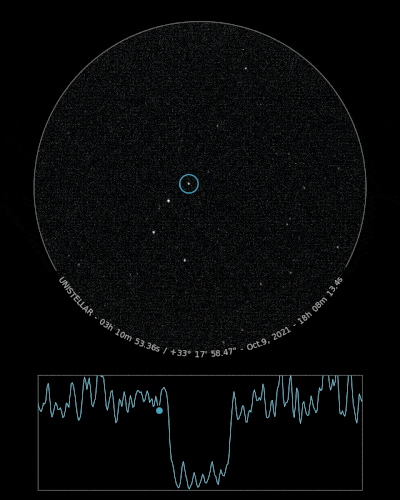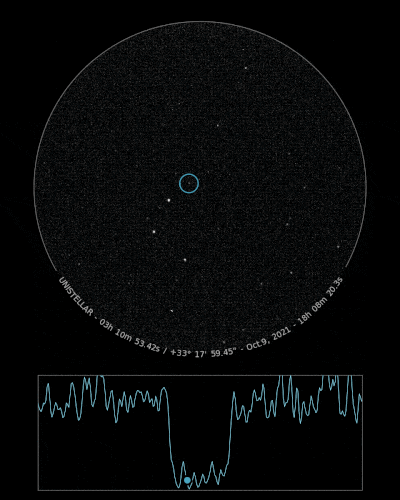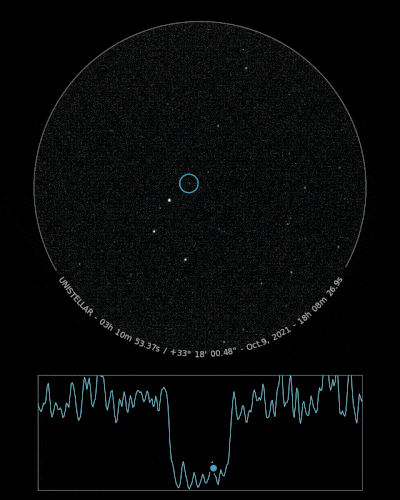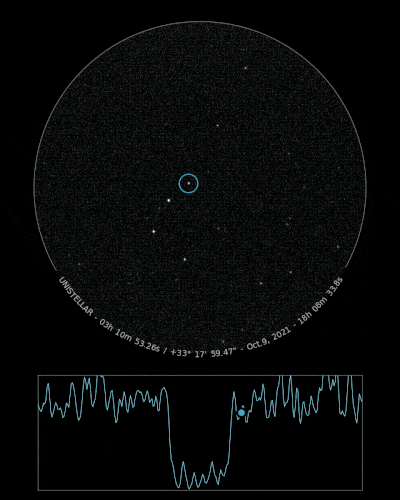
If you detect the shadow of Loreley, we can refine our understanding of its trajectory, size, and shape!
Check out our Asteroid Occultation Predictions page for more details on this occultation including location, timing, and more.
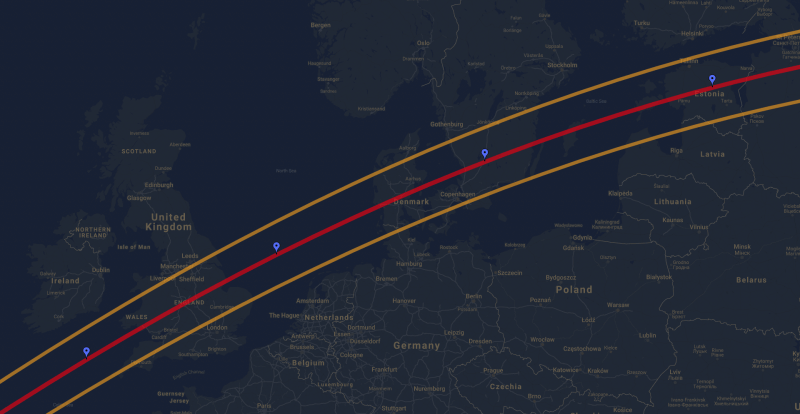
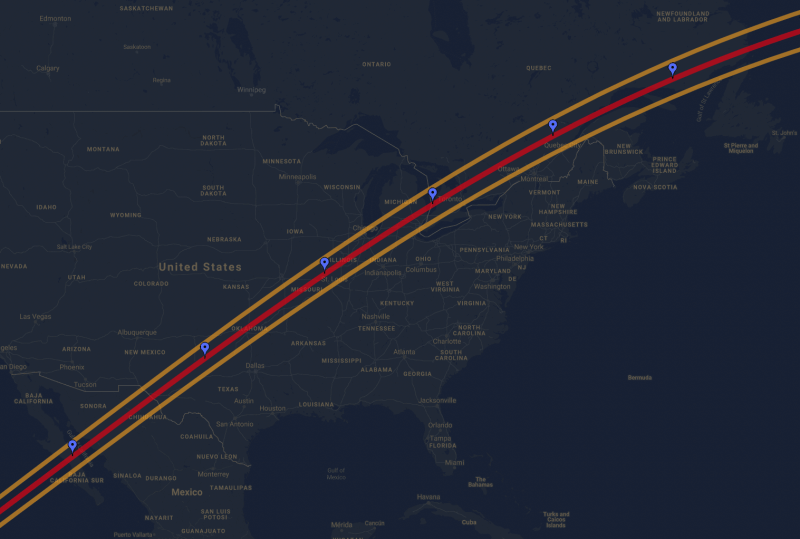
- Depending on your location, click on Western Europe or North America in the drop-down menu
- Scroll down the page until you find 165 Loreley. Then, click on it.
- A map of Western Europe or North America with the path of the occultation should appear below.
- Zoom into the map so you can see the exact location where you can observe this occultation.
- Check the information above the map to make sure you have the correct parameters and observe for the correct duration.
If you have any questions, please reach out to us at [email protected].
Further readings
Titan’s shadows
Every month, discover three unmissable celestial events to observe with your Unistellar telescope.
3 Reasons to observe this month
Every month, discover three unmissable celestial events to observe with your Unistellar telescope.
Observing Eclipses on Jupiter: Cosmic Spectacles Through a Telescope
The latest Unistellar App Update, version V3.0, is now live. Explore a smooth stargazing experience !
Unistellar Community Included In Multiple Scientific Papers
Did you know Unistellar Citizen Astronomers are often cited in published scientific papers? Find out how you can contribute too!
What Are the Names of All the Full Moons in 2024?
Discover the enchanting names of the full moons in 2024. Delve into the unique character of each lunar spectacle and embrace the allure of the night sky.
New Unistellar App Update: Version 3.0
The latest Unistellar App Update, version V3.0, is now live. Explore a smooth stargazing experience !